5 Key Tips for Optimal Marine Auxiliary Battery Performance and Safety
An auxiliary battery in marine applications is vital for powering essential systems like lighting, navigation equipment, and electronics during periods when the main engine is off. Selecting the right size, type (such as lead-acid or lithium-ion), and considering factors like voltage, capacity, and…….
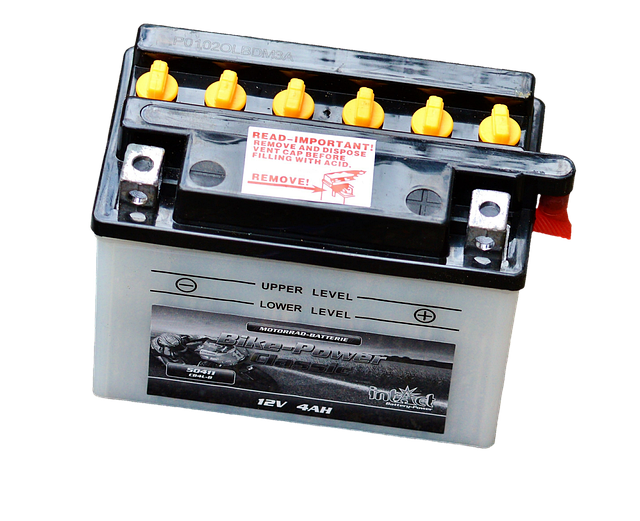

An auxiliary battery in marine applications is vital for powering essential systems like lighting, navigation equipment, and electronics during periods when the main engine is off. Selecting the right size, type (such as lead-acid or lithium-ion), and considering factors like voltage, capacity, and deep-cycle capabilities tailored to your vessel's needs is crucial for performance and safety at sea. Installation should ensure the battery is secure, well-ventilated, and positioned to dissipate heat, with non-conductive straps and appropriate cables to prevent damage from vibrations or movement. Regular maintenance, including monitoring water levels in flooded batteries, visual inspections for corrosion, and using charging systems that prevent overcharging, is essential for longevity. Auxiliary battery management systems (ABMS) are advanced tools that actively monitor and control various aspects of the battery's operation to optimize its lifespan and prevent damage from extreme conditions. Proper selection, installation, maintenance, and the use of an ABMS are vital for ensuring a reliable power source on marine vessels and safeguarding against operational disruptions and potential hazards. Adhering to safety protocols during installation and consistent upkeep will protect against malfunctions and extend the auxiliary battery's service life.
Navigating the high seas requires robust and reliable power sources, and auxiliary batteries play a pivotal role in ensuring the smooth operation of marine vessels. This article delves into five essential tips for optimizing your vessel’s auxiliary battery performance, from selection to maintenance. Whether you’re an experienced mariner or a novice, understanding how to choose, install, and manage your auxiliary battery is crucial for your journey’s success. From the vital role they play in critical systems to the best practices for charging and discharging, these tips will help safeguard against failures and common issues, keeping you powered and prepared on the open water.
- Understanding Auxiliary Battery Roles on Vessels
- Selecting the Right Auxiliary Battery for Your Marine Vessel
- Proper Auxiliary Battery Installation and Maintenance
- Optimizing Performance with Auxiliary Battery Management Systems
- Best Practices for Charging and Discharging Your Auxiliary Battery
- Safety Precautions to Prevent Auxiliary Battery Failures
Understanding Auxiliary Battery Roles on Vessels

When it comes to marine applications, an auxiliary battery plays a pivotal role in ensuring that a vessel’s operations are smooth and efficient, especially when the primary engine-driven systems are not in use. These batteries are designed to supply power for onboard electrical needs such as navigation lights, interior lighting, onboard electronics, and other ancillary systems. Unlike the starter battery which is solely responsible for starting the engine, the auxiliary battery is sized to run the boat’s appliances and systems for extended periods without the need for the engine to be running. Understanding the importance of an auxiliary battery’s role requires a grasp of several factors, including the vessel’s power requirements, the nature of marine activities, and the types of batteries available.
Selecting the right auxiliary battery involves considering factors such as capacity, voltage, and type (lead-acid, AGM, or lithium-ion). The capacity must be sufficient to handle all ancillary loads without depleting the charge too quickly. Voltage must match the boat’s electrical system, which is typically 12 volts for small boats and may be 24 volts for larger vessels. Additionally, the battery type should align with considerations such as maintenance requirements, deep-cycle capabilities, and lifespan under the expected usage conditions. Properly sizing and installing an auxiliary battery ensures that it can handle the demands placed upon it, providing reliable power for all auxiliary systems, from fish finders to refrigeration units, thereby enhancing the overall safety and functionality of the vessel.
Selecting the Right Auxiliary Battery for Your Marine Vessel

When selecting an auxiliary battery for your marine vessel, it’s crucial to consider several factors to ensure optimal performance and reliability on the water. The marine environment is harsh, with saltwater corrosion and vibrations posing significant challenges for any electrical system. A durable and high-quality auxiliary battery will withstand these conditions, maintaining power for your essential equipment and accessories. Firstly, consider the size of your vessel and available space where the battery will be installed. The battery must fit securely to prevent movement that could cause internal damage during operation. Secondly, assess the types of activities you’ll be engaging in. Frequent use of electronics like fishfinders, GPS units, or VHF radios demands a battery with a high ampere-hour (Ah) rating and the ability to handle multiple discharge/recharge cycles without compromising performance. Additionally, opt for batteries designed specifically for marine applications, as they often come with built-in hydrogen gas recombination technology to enhance safety and longevity. By carefully selecting an auxiliary battery tailored to your vessel’s needs and usage patterns, you ensure a reliable power source that enhances the enjoyment and safety of your maritime experiences.
Proper Auxiliary Battery Installation and Maintenance
When integrating an auxiliary battery into your marine setup, proper installation and ongoing maintenance are paramount for optimal performance and longevity. The initial step in installation involves selecting a suitable location that allows for effective heat dissipation. This is because batteries produce heat during operation, and excessive temperatures can diminish battery life and efficiency. Secure the battery in a non-tipping position, ensuring it’s mounted within a well-ventilated compartment to prevent gas buildup, which can be hazardous. Use sturdy, non-conductive straps to hold the battery in place and connect it to the boat’s electrical system. It’s imperative to use the correct size and type of cables to minimize voltage drop and ensure a reliable connection.
Maintenance of your auxiliary battery is equally crucial. Regularly check the water levels in flooded lead-acid batteries, adding distilled water as necessary to maintain the electrolyte solution. For maintenance-free batteries, regular inspections are still required to monitor the condition of the battery and its terminals. Clean any corrosion from terminals and connectors, and apply a protective coating to prevent future corrosion. Routine testing of the battery’s charge level with a hydrometer or voltmeter is essential, as is ensuring that all charging systems are set correctly to avoid overcharging, which can shorten the battery’s life. Storing your boat and its auxiliary battery in a cool, dry place during off-season months will also contribute to its extended service life. By adhering to these maintenance practices, you can ensure your auxiliary battery serves you reliably for many years on the water.
Optimizing Performance with Auxiliary Battery Management Systems

When integrating an auxiliary battery into marine applications, performance optimization is paramount. Auxiliary battery management systems play a crucial role in maintaining the longevity and efficiency of the battery. These sophisticated systems monitor and regulate various parameters such as voltage, current flow, temperature, and state of charge to ensure the battery operates within its ideal range. By doing so, they prevent overcharging or deep discharge conditions that can harm the battery’s performance and shorten its lifespan. Users can benefit from extended service intervals due to the reduced strain on the main engine alternator, as the auxiliary system can handle varying loads more effectively. Furthermore, these management systems are designed with smart algorithms that adapt to different usage patterns, thereby maximizing the battery’s capacity and ensuring that it is ready for use when needed. Proper installation and configuration of an auxiliary battery management system not only enhance the overall marine experience but also provide peace of mind by safeguarding one of the most critical components on board.
Best Practices for Charging and Discharging Your Auxiliary Battery
When managing an auxiliary battery, particularly in marine applications, adhering to best practices for charging and discharging is crucial for prolonging its lifespan and ensuring reliable power when needed. Firstly, it’s imperative to select a charging system that matches the battery type and capacity. For instance, lead-acid auxiliary batteries typically require a charger with a compatible voltage and amperage settings. Regular maintenance charging, even when not in use, helps prevent sulfation and keeps the battery ready for service. Additionally, avoid overcharging, as it can significantly reduce the battery’s efficiency and shorten its lifespan.
During discharging, it’s important to monitor the battery’s state of charge to prevent deep discharges, which can be damaging. Auxiliary batteries should not be allowed to drop below 50% of their capacity. When designing or outfitting a vessel, ensure that the electrical system is equipped with a proper load management and circuit protection system. This includes the use of appropriate fuses or circuit breakers to safeguard against short circuits or overloads that could lead to battery damage or fire hazards. Regularly checking the battery’s voltage and ensuring it doesn’t fall below its recommended discharge threshold is a proactive step in maintaining its health. By following these guidelines for charging and discharging your auxiliary battery, you can enhance its performance and extend its operational life, ensuring that when you set sail or venture into remote waters, you have a dependable power source at your disposal.
Safety Precautions to Prevent Auxiliary Battery Failures

When integrating auxiliary batteries into marine applications, safety precautions are paramount to prevent failures that could compromise the vessel’s operation and endanger passengers. To mitigate risks associated with auxiliary battery systems, it is crucial to adhere to a set of guidelines ensuring both reliability and safety. Firstly, the installation should comply with all relevant standards and regulations, which include proper placement to avoid damage from impact or excessive heat. Additionally, all connections should be made using heavy-gauge, corrosion-resistant cable and appropriate fittings, ensuring that terminals are securely tightened to prevent loose connections that could lead to short circuits or overheating.
Regular maintenance is another key factor in preventing auxiliary battery failures. This involves periodic checks on the battery’s charge levels, as well as inspecting the battery case for cracks and ensuring that terminal connections are clean, tight, and free from corrosion. Users should also be familiar with the marine battery’s manufacturer’s guidelines, which provide specific maintenance recommendations tailored to their product. Employing a charging system with automatic voltage adjustment can further protect the battery by preventing overcharging, which is a common cause of auxiliary battery failure. By prioritizing safety and regular upkeep, users can significantly reduce the likelihood of auxiliary battery malfunctions while on the water.
When navigating the vast expanse of marine applications, having a reliable auxiliary battery is paramount. The five essential tips outlined in this article—covering understanding roles, selecting the right type, proper installation and maintenance, optimizing performance through management systems, and best practices for charging and discharging—form the cornerstone of auxiliary battery management. By adhering to these guidelines, mariners can ensure their vessels are equipped with a robust power source that enhances safety and operational efficiency. Remember to consistently follow these tips to maintain your marine vessel’s auxiliary battery in optimal condition, guaranteeing a seamless journey on the water.







